Kubernetes for Developers #16: Kubernetes Service Types - ClusterIP, NodePort, LoadBalancer and ExternalName
In the previous article (Kubernetes for Developers #15: Kubernetes Service YAML manifest in-detail) we have seen how to create K8 Service and access the Pods inside the cluster.
1. ClusterIP
- It exposes the service within the Kubernetes cluster only.
- Only Pods within the K8 Cluster can communicate using this service. You cannot access directly from the browser using Service IP.
- Kubernetes controller creates unique virtual IP address (i.e., which is called ClusterIP) whenever the service is created.
- This is the default serviceType
As per above diagram,
- The K8 service "nginx-service" has been created with "ClusterIP" type.
- nginx-service mapped to Pod labels app:nginx
- nginx-service mapped service port 8081(i.e. Port ), container port 80 (i.e. targetPort )
- As it is "ClusterIP" type, we can't access the service outside the cluster. So, enter into any Pod and make curl using service IP or name or FQDN (<servicename>.<namespace>.svc.cluster.local) i.e. curl http://10.107.40.61:8081 (or) curl http://nginx-service:8081 (or) curl http://nginx-service.default.svc.cluster.local:8081
Before creating service, first create K8 Deployment and make nginx Pods are up and running with label app:nginx
Read complete article on k8 deployment @ Kubernetes for Developers #14: Kubernetes Deployment YAML manifest in-detail
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment
spec:
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.14.2
ports:
- containerPort: 80
// Create a Deployment based on YAML file
$ kubectl apply -f ./nginx-deployment.yaml
deployment.apps/nginx-deployment created
// Display information about all deployments
$ kubectl get deployments
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
nginx-deployment 2/2 2 2 64s
// Display information about Pods with labels
$ kubectl get pods --show-labels
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE LABELS
nginx-deployment-6b474476c4-8mx72 1/1 Running 0 30h app=nginx
nginx-deployment-6b474476c4-cdhvb 1/1 Running 0 30h app=nginx
Create ClusterIP Service using YAML manifest
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx-service
spec:
type: ClusterIP
selector:
app: nginx
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 8081
targetPort: 80
// Create a Service using YAML file
$ kubectl apply -f ./nginx-service-cluserIP.yaml
service/nginx-service created
// Display information about Services
$ kubectl get services
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
nginx-service ClusterIP 10.105.224.36 <none> 8081/TCP 112s
// Display information about the Endpoints
$ kubectl get endpoints
NAME ENDPOINTS AGE
nginx-service 10.1.1.61:80,10.1.1.63:80 19m
NAME: Name of the Endpoint which is same as Service name
ENDPOINTS: list all the Pod IPs where label as app:nginx
// Enter into nginx Pod shell
$ kubectl exec -it nginx-deployment-6b474476c4-8mx72 -- bin/bash
// update packages
# apt-get update
// install curl
# apt-get install curl
// make curl using service name(or IP ) and port to access nginx webpage
# curl http://nginx-service:8081
(or)
# curl http://10.105.224.36:8081
There is another way to test service by port-forwarding from service port to local computer port
// use kubectl port-forward to test the service in local computer
$ kubectl port-forward service/nginx-service 8081:8081
Forwarding from 127.0.0.1:8081 -> 80
Forwarding from [::1]:8081 -> 80
// Go to browser and hit http://localhost:8081 to view nginx webpage
2. NodePort
- It exposes the service both in and outside the cluster
- It exposes the service on each Worker Node’s IP at a static port (i.e., which is called NodePort).
- A ClusterIP Service will be created automatically whenever the NodePort service is created. It means, The external traffic enter into the cluster using <NodeIP>:<NodePort> (ex: 100.72.40.61 : 30010) and it direct traffic to the ClusterIP
- NodePort must be within the range from 30000-32767
As per above diagram,
- The K8 service "nginx-service" has been created with "NodePort" type.
- nginx-service mapped to Pod labels app:nginx
- nginx-service mapped service port 8081(i.e. Port ), container port 80 (i.e. targetPort ) and node Port 30010
- As it is "NodePort" type, we can access the service both inside and outside the cluster .
- To access inside cluster, enter into any Pod and make curl using service IP or name or FQDN (<servicename>.<namespace>.svc.cluster.local) i.e. curl http://10.107.40.61:8081 (or) curl http://nginx-service:8081 (or) curl http://nginx-service.default.svc.cluster.local:8081
- To access outside cluster, go to browser and hit http://<nodeIP>:<nodePort> i.e. http://100.17.20.31:30010
Create NodePort Service using YAML manifest
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx-service
spec:
type: NodePort
selector:
app: nginx
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 8081
targetPort: 80
nodePort: 30010
// Create a Service using YAML file
$ kubectl apply -f ./nginx-service-nodeport.yaml
service/nginx-service created
// Display information about Services
$ kubectl get services
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/nginx-service NodePort 10.105.224.36 <none> 8081:30010/TCP 15h
K8 Endpoint object will be created automatically when the Service is created with same service name. It will track all the Pod IPs where label as app:nginx
// Display information about the Endpoints
$ kubectl get endpoints
NAME ENDPOINTS AGE
nginx-service 10.1.1.61:80,10.1.1.63:80 19m
NAME: Name of the Endpoint which is same as Service name
ENDPOINTS: list all the Pod IPs where label as app:nginx
Go to browser and enter http://100.17.20.31:30010 to view nginx webpage.
Go to browser and enter http://localhost:30010 if you are testing locally using docker-desktop or minikube.
Go to browser and enter http://localhost:30010 if you are testing locally using docker-desktop or minikube.
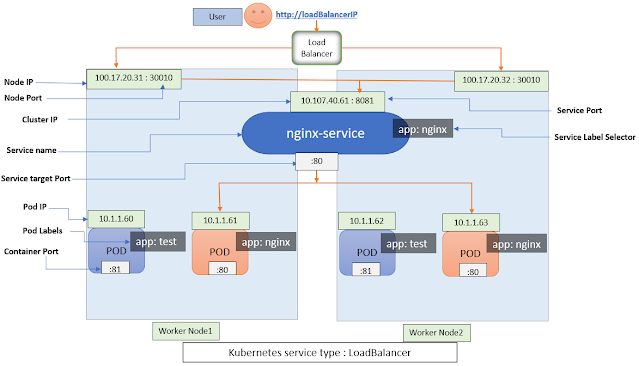
3. LoadBalancer
- It exposes the service both in and outside the cluster
- It exposes the service externally using cloud providers load balancer.
- NodePort and ClusterIP services will be created automatically whenever the LoadBalancer service is created.
- The LoadBalancer service redirects traffic to the node port across all the nodes.
- The external clients connect to the service through load balancer IP
- The is the most preferable approach to expose service outside the cluster
As per above diagram,
- The K8 service "nginx-service" has been created with "LoadBalancer" type.
- nginx-service mapped to Pod labels app:nginx
- nginx-service mapped service port 8081(i.e. Port ), container port 80 (i.e. targetPort ) and node Port 30010
- As it is "LoadBalancer" type, we can access the service both inside and outside the cluster .
- To access inside cluster, enter into any Pod and make curl using service IP or name or FQDN (<servicename>.<namespace>.svc.cluster.local) i.e. curl http://10.107.40.61:8081 (or) curl http://nginx-service:8081 (or) curl http://nginx-service.default.svc.cluster.local:8081
- To access outside cluster, go to browser and hit http://<loadBalancerIP> i.e. http://2343260762.us-east-1.elb.amazonaws.com
Create LoadBalancer Service using YAML manifest
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx-service
spec:
type: LoadBalancer
selector:
app: nginx
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 8081
targetPort: 80
nodePort: 30010
// Create a Service using YAML file
$ kubectl apply -f ./nginx-service-lb.yaml
service/nginx-service created
// Display information about Services
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/nginx-service LoadBalancer 10.105.224.36 2343260762.us-east-1.elb.amazonaws.com 8081:30010/TCP 2h
Go to browser and enter http://2343260762.us-east-1.elb.amazonaws.com to view nginx webpage.
Go to browser and enter http://localhost:30010 if you are testing locally using docker-desktop or minikube.
Go to browser and enter http://localhost:30010 if you are testing locally using docker-desktop or minikube.
4. ExternalName
- It maps service to a DNS name , typically domain/subdomain name (ex: foo.example.com )
- It will redirect a request to domain specified in the externalName
- There won't be any difference while accessing service inside Pod. (i.e it should be external-service.default.svc.cluster.local )
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: external-service
spec:
type: ExternalName
externalName: example.api.com
// Create a Service using YAML file
$ kubectl apply -f ./external-service.yaml
service/external-service created
// Display information about Services
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/external-service ExternalName <none> example.api.com <none> 9m31s
Kubernetes for Developers Journey.
- Kubernetes for Developers #25: PersistentVolume and PersistentVolumeClaim in-detail
- Kubernetes for Developers #24: Kubernetes Volume hostPath in-detail
- Kubernetes for Developers #23: Kubernetes Volume emptyDir in-detail
- Kubernetes for Developers #22: Access to Multiple Clusters or Namespaces using kubectl and kubeconfig
- Kubernetes for Developers #21: Kubernetes Namespace in-detail
- Kubernetes for Developers #20: Create Automated Tasks using Jobs and CronJobs
- Kubernetes for Developers #19: Manage app credentials using Kubernetes Secrets
- Kubernetes for Developers #18: Manage app settings using Kubernetes ConfigMap
- Kubernetes for Developers #17: Expose service using Kubernetes Ingress
- Kubernetes for Developers #16: Kubernetes Service Types - ClusterIP, NodePort, LoadBalancer and ExternalName
- Kubernetes for Developers #15: Kubernetes Service YAML manifest in-detail
- Kubernetes for Developers #14: Kubernetes Deployment YAML manifest in-detail
- Kubernetes for Developers #13: Effective way of using K8 Readiness Probe
- Kubernetes for Developers #12: Effective way of using K8 Liveness Probe
- Kubernetes for Developers #11: Pod Organization using Labels
- Kubernetes for Developers #10: Kubernetes Pod YAML manifest in-detail
- Kubernetes for Developers #9: Kubernetes Pod Lifecycle
- Kubernetes for Developers #8: Kubernetes Object Name, Labels, Selectors and Namespace
- Kubernetes for Developers #7: Imperative vs. Declarative Kubernetes Objects
- Kubernetes for Developers #6: Kubernetes Objects
- Kubernetes for Developers #5: Kubernetes Web UI Dashboard
- Kubernetes for Developers #4: Enable kubectl bash autocompletion
- Kubernetes for Developers #3: kubectl CLI
- Kubernetes for Developers #2: Kubernetes for Local Development
- Kubernetes for Developers #1: Kubernetes Architecture and Features
Happy Coding :)


The output IP of `kubectl get services` didn't correspond to the IP in figures
ReplyDelete